Key Notes
Here are some key takeaways about welding:
Take away from the blog post
- Welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal together by melting and fusing them using heat, pressure, or both.
- Welding is used in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, construction, and automotive repair.
- There are several different types of welding processes, including MIG, TIG, Stick, and Flux-Cored welding, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Some factors to consider when choosing a welding process include the type of metal being welded, the thickness of the metal, and the desired appearance of the weld.
- Welding requires proper training, equipment, and safety precautions to prevent injury and ensure a high-quality weld.
- Overall, welding is a versatile and widely used process for joining metal and is essential in many industries. The choice of welding process depends on several factors, including the type and thickness of metal being welded, as well as the desired appearance of the finished weld. Proper training, equipment, and safety precautions are necessary to ensure a successful and safe welding process.
What is Welding? You will get details guideline about Welding through this blog post. Welding is a process of joining two or more pieces of metal by heating them to a molten state and then allowing them to cool and solidify into a strong and durable bond. This process is used in a wide range of industries, including construction, manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace.
The welding process involves the use of heat, pressure, and sometimes filler material to create the bond between the two metal pieces. The heat is usually generated by an electric arc or a flame, and the pressure is applied through a variety of methods, including manual force or mechanical devices.
Welding is an important skill that requires specialized training and knowledge of metallurgy, physics, and safety procedures. Skilled welders are in high demand, as their work is essential to many industries and applications.
What is Welding?
Welding is the process of using heat, pressure, or both to join two or more pieces of metal together. The goal of welding is to join two pieces of metal together in a way that will last. Welding is often used to join metal parts together in building, manufacturing, and repair, among other fields. There are many different ways to weld, and each one has its own benefits and drawbacks. Some of the most popular ways to weld are MIG, TIG, Stick, and Flux-Cored. To make sure that welding is done well and safely, you need the right training, tools, and safety measures. When done right, welding can make a strong and long-lasting link between two pieces of metal. This makes it an important process in many situations.
How Does Welding Work?
Welding is the process of joining together two or more pieces of metal or thermoplastic by melting and fusing the surfaces together. There are many different ways to weld, but the basic idea is always the same.
Here are the main steps in the process of welding:
- Preparation: Before welding, the metal or thermoplastic pieces need to be cleaned and prepared to make sure the bond is strong. This means getting rid of any dirt, rust, or paint and putting the pieces in the right place.
- Heat: During the welding process, heat is used to melt the metal or thermoplastic on the surface. The heat can come from a gas flame, an electric arc, or a laser.
- Filler material: Sometimes, a filler material is used to make the weld stronger. Usually, this is a metal wire that melts together with the two surfaces.
- Fusion: The surfaces are fused together when they are heated to the point where they will melt. This makes the two pieces of material stick together very well.
- Cooling: Once the weld is finished, the material is left to cool and harden. This makes sure the bond is strong and lasts a long time.
The type of material being welded and the welding technique will both affect how the welding is done. Gas welding, arc welding, and resistance welding are all common ways to weld.
Joining Metals, Woods and Plastics by Welding Process
When welding metals, wood, and plastics together, you have to use different methods for each type of material. Here are some of the most common ways to weld each material:
Joining Metals
There are many ways to weld metals together, including:
- Gas welding: In this method, a flame is used to heat the metal surfaces, which are then joined by melting a filler rod between them.
- Arc welding: This method uses an electric arc to heat the metal surfaces, which are then joined by melting a filler rod in between them. There are different ways to do arc welding, such as TIG welding (tungsten inert gas), MIG welding (metal inert gas), and stick welding.
- Resistance welding: This method uses heat and pressure to join two pieces of metal together. Spot welding, seam welding, and projection welding are all types of resistance welding.
Joining Woods
There are several ways to join wood together:
Joining Plastics
The following methods can be used to join plastics:
Ultrasonic welding: This method uses high-frequency vibrations to make friction between the plastic surfaces, which causes the surfaces to melt and join together.
Hot plate welding: This method involves heating a metal plate, pressing it onto the plastic surfaces, and letting the surfaces melt and join together.
Laser welding: In this method, the plastic surfaces are heated with a laser, which makes them melt and stick together.
The type of material being joined and the needs of the application will determine which welding method is used.
Common Joint Configurations of Welding
Joint configurations are the shapes and orientations of the parts that are being joined. They are a very important part of how strong and long-lasting a welded joint will be. Here are some common ways to set up joints for welding:
- Butt Joint: A butt joint is made when the edges of two pieces of material are joined. This is the most common and easiest way to set up a joint, but it tends to be the weakest.
- Lap Joint: Two pieces of material that overlap each other make a lap joint. This type of joint is stronger than a butt joint, but it takes more material to make.
- T-Joint: When two pieces of material are joined at a right angle, they make a T-joint. This joint arrangement is strong in one direction, but it can be weaker in the other.
- Corner Joint: When two pieces of material are joined at a corner, this is called a corner joint. This type of joint is strong in both directions, but it can be hard to put together correctly.
- Edge Joint: An edge joint is made when the edges of two pieces of material that aren’t the same size are joined together. This type of joint is stronger than a butt joint, but it takes more material to make.
- Joints for welding pipes: There are different kinds of joints for welding pipes, like the butt joint, the socket weld joint, and the fillet weld joint. These joints are made to give pipes the most strength and durability.
Several things, like the type of material being welded, how strong the joint needs to be, and how it will be welded, will affect the choice of joint configuration. The welder must carefully choose the right joint configuration to make sure the weld is strong and lasts a long time.
Different Kinds of Welding Process Based on Penetration
The level of penetration achieved during the welding process can be used to classify welds.
Full penetration weld
A full penetration weld is a type of welding joint in which the welding process goes all the way through the base material, fusing the two metal pieces together completely. This type of weld is often used when a high-strength weld is needed, such as in structural steelwork, pressure vessels, and piping.
Different types of welding, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW or TIG), gas metal arc welding (GMAW or MIG), and shielded metal arc welding, can be used to make full penetration welds (SMAW or stick welding). In all cases, the welding process is carefully controlled to make sure that the weld pool goes all the way through the base material and that there are no gaps or voids in the weld.
Full penetration welds are usually stronger and last longer than other types of welds because they completely melt the metal pieces that are being joined together. Since there are no weak spots or gaps in the weld, they are also less likely to break under stress or load. But to get a full penetration weld, you need a lot of skill, experience, and to pay close attention to the welding process and parameters.
Partially penetrating weld
A partial penetration weld is a type of weld where the welding process only goes partway through the thickness of the base material. This means that the metal parts being joined only partially melt together. This type of weld is often used when a full penetration weld is not needed, such as in non-critical structures, general fabrication, and decorative work.
Different types of welding, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW or TIG), gas metal arc welding (GMAW or MIG), and shielded metal arc welding, can be used to make partial penetration welds (SMAW or stick welding). In all cases, the welding process is carefully controlled to make sure that the weld pool only goes partway through the thickness of the base material, leaving a space or void between the two pieces being joined.
Partially penetrating welds are usually not as strong or long-lasting as fully penetrating welds because they don’t fully fuse the two metal pieces being joined. But they can be made faster and cheaper than full penetration welds because they need less welding material and less time to make. Partially penetrating welds are also less likely to cause the base material to distort or warp because they use less heat.
Welding Process Based on Accessibility
Accessibility is another way to divide welding joints. This means how easy it is to get to the joint while welding. Based on how easy they are to reach, the main types of welds are:
Flat position welds: This type of weld is done on a flat surface where the joint is easy to reach from both sides. Flat position welds are often used when making things out of sheet metal and in general welding.
Horizontal position welds: are done on a horizontal surface where the joint can be reached from one side. In structural welding and pipe welding, horizontal welds are often used.
Vertical position welds: Welds in a vertical position are done on a vertical surface where the joint can be reached from one side. Welds in a vertical position are often used when building ships, buildings, and bridges.
Overhead position welds: This type of weld is done on a surface that is above the joint and can only be reached from one side. Welds in the overhead position are often used in building and shipbuilding.
Inaccessible welds: Welds that can’t be reached: This type of welding is done in a place where the joint is hard to get to. Welds that are hard to get to often need special techniques and tools, like robotic welding or welding mirrors, to be done.
Access to the weld joint can have a big effect on the welding process because it can affect the weld’s quality and strength. Welds that are hard to get to may need more complicated welding techniques and may be more likely to have flaws or not fuse completely. Skilled welders can get around these problems and make high-quality welds in any position by using a variety of methods.
Features of Things About Welds That Are Done
Different things, like the welding process, the type of joint being welded, the type of metal being welded, and the welding parameters, affect how a weld looks when it’s done. But there are some general things you can expect from a finished weld:
- Fusion: When a weld is done, the most important thing is that the two metals that are being joined melt together. The parent metal and the filler metal should completely melt together in a good weld.
- Penetration: Another important feature is the depth of penetration of the weld. The penetration should be deep enough to make sure the weld is strong and can handle the stresses needed.
- Join the bead: The raised part of a weld that forms during the welding process is called the weld bead. A good weld should have a weld bead that is smooth, even, and free of cracks or other flaws.
- Heat affected zone: The area around the weld where the metal has been heated and cooled during the welding process is called the heat affected zone (HAZ). The HAZ should not have any cracks, dents, or other problems that could weaken the weld.
- Shape of the weld: Depending on the type of joint being welded and the welding process used, the shape of the finished weld can be different. But the weld should usually look smooth and even, like the parent metal, so that it doesn’t stand out.
6.Strength: Another important thing is how strong the weld is when it’s done. A good weld should be strong enough to hold up under the required loads and stresses without breaking. Various destructive and non-destructive testing methods can be used to check the strength of the weld.
What are the different Types of welding, and what do they do?
Welding is the process of joining two or more pieces of metal or thermoplastics together with heat and/or pressure to make a strong and permanent bond. There are different ways to weld, and each one has its own advantages and uses. Here are some common ways to weld and what they are used for:
- Arc Welding: This type of welding uses an electric arc to heat and melt the metal, which then cools and hardens to form a bond. Arc welding is often used in building, making, and fixing things, and it can be done with either AC or DC power.
- Gas Welding: In this method, the metal being welded is heated and melted by a flame made from burning gases like acetylene and oxygen. Gas welding is often used to fix cars, work with metal, and make sculptures.
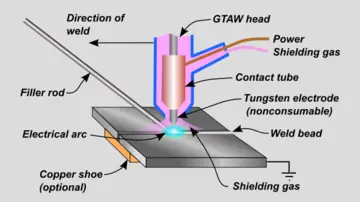
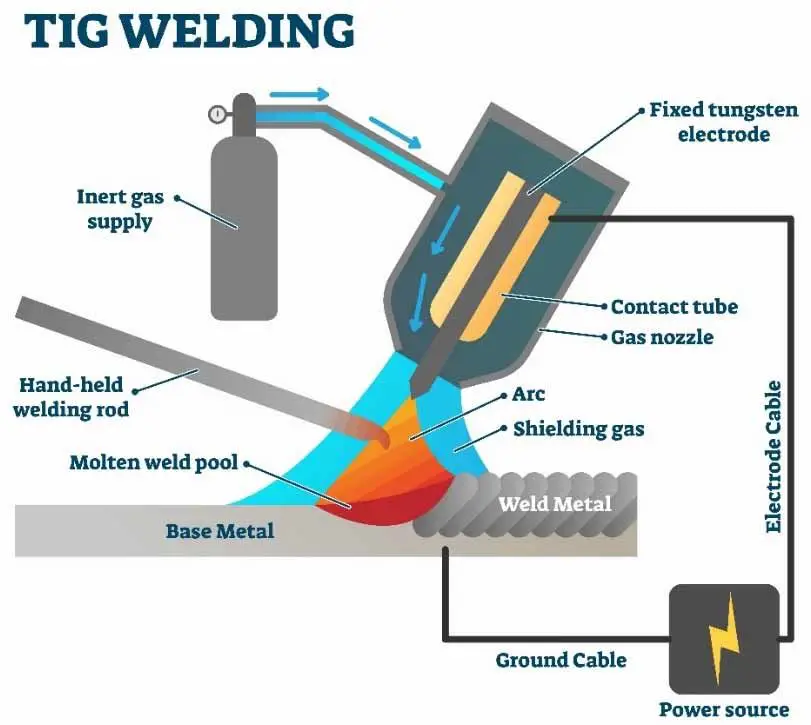
- TIG Welding: Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding is a precise welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to make the arc and a shielding gas to protect the weld from contamination from the air. TIG welding is used a lot in the nuclear, aerospace, and auto industries.
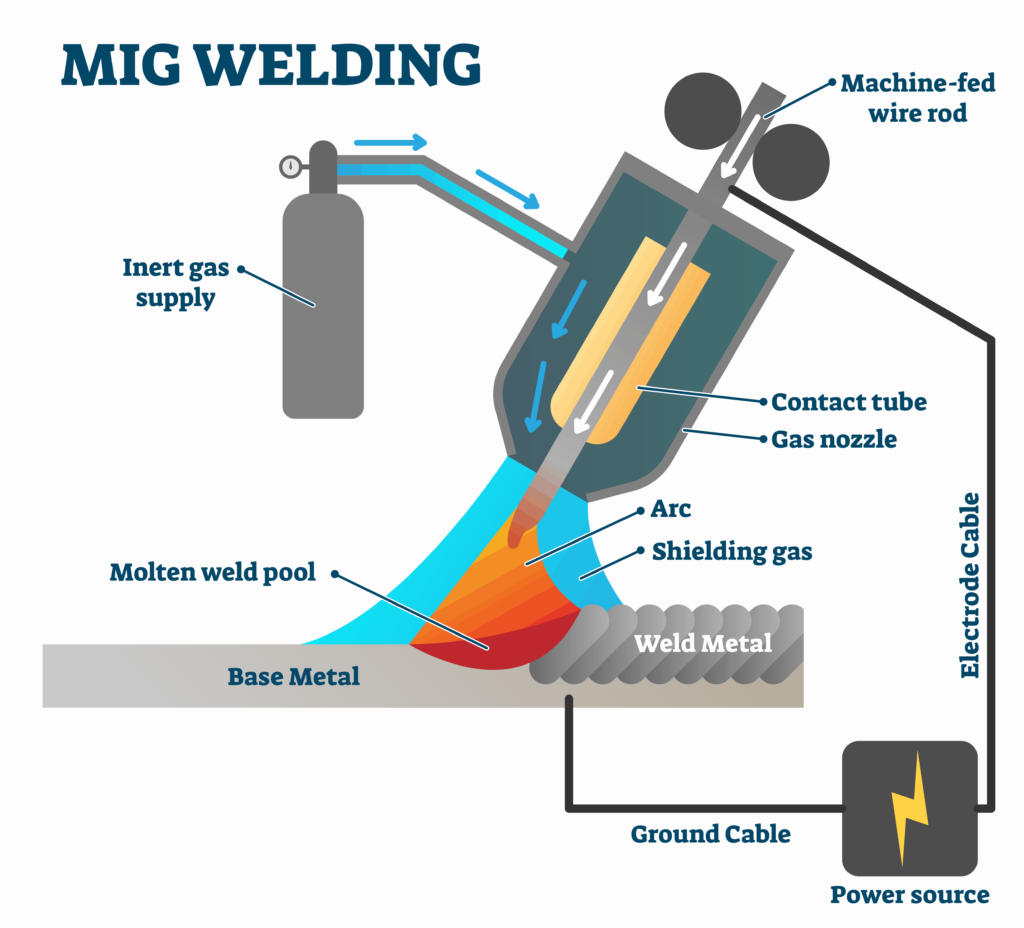
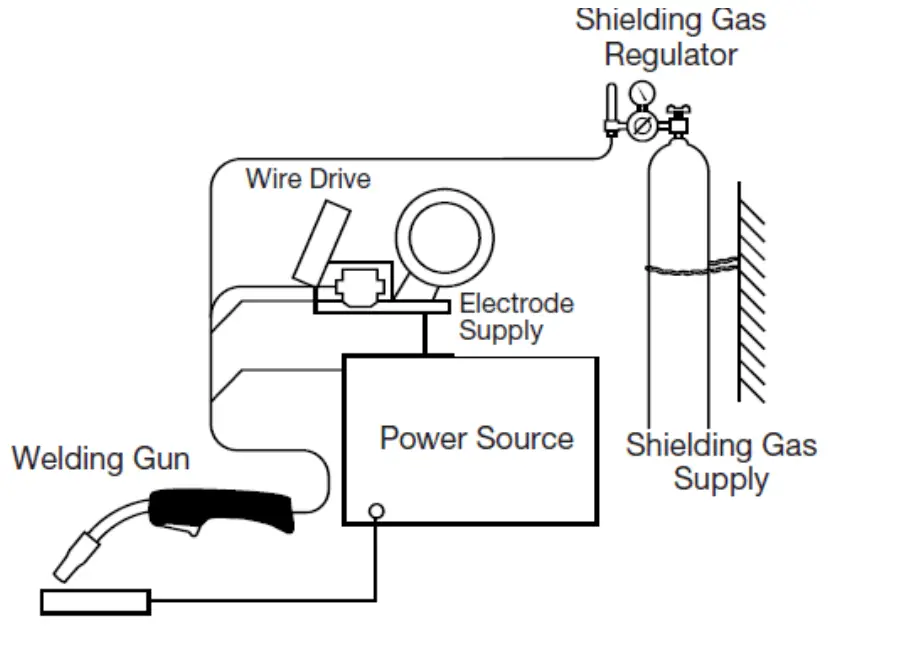
- MIG Welding: In Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding, a consumable wire electrode is fed into the weld pool using a wire-fed welding gun. After that, the wire is melted and used to make the bond. MIG welding is used a lot in the construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries.
- Flux-Cored Arc Welding: This method is similar to MIG welding, but instead of a solid wire, it uses a hollow wire filled with flux to protect the weld from contamination from the air. Flux-cored arc welding is often used to build ships, fix heavy equipment, and build things.
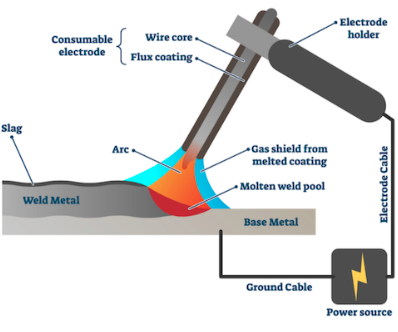
- Stick Welding: This type of welding, which is also called Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), uses a flux-coated stick electrode to make the arc and protect the weld from getting dirty from the air. Stick welding is a common way to build, fix, and keep things in good shape.
- Laser Welding: In laser welding, a powerful laser beam is used to melt and join metal pieces together. This method is often used in the electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries.
Overall, the type of welding used depends on the type of material being joined, how strong the bond needs to be, and what the finished product will be used for.
There are 4 Common Ways to weld.
There are different ways to weld, and each one has its own advantages and uses. Here are the four most common methods of welding:
MIG Welding
Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding is a type of welding in which a wire electrode is fed into the weld pool using a wire-fed welding gun. After that, the wire is melted and used to make the bond. MIG welding is used a lot in the construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries.
TIG Welding
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding is a precise welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to make the arc and a shielding gas to protect the weld from contamination from the air. TIG welding is used a lot in the nuclear, aerospace, and auto industries.
Stick Welding
This type of welding, which is also called Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), uses a flux-coated stick electrode to make the arc and protect the weld from contamination from the air. Stick welding is a common way to build, fix, and keep things in good shape.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding
This method is similar to MIG welding, but instead of a solid wire, it uses a hollow wire filled with flux to protect the weld from contamination from the air. Flux-cored arc welding is often used to build ships, fix heavy equipment, and build things.
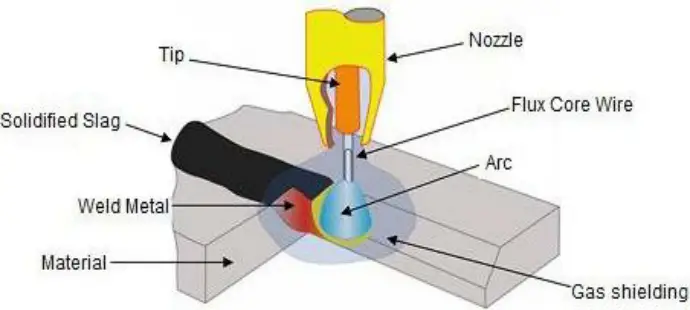
Overall, the type of welding process used depends on things like the material being welded, how strong the bond needs to be, and what the finished product will be used for. To make sure a strong, long-lasting bond, it’s important to choose the right type of welding process for each job.
Sources of Power for Welding
Most welding is done with electricity, but there are other ways to do it as well. The main sources of energy used in welding are:
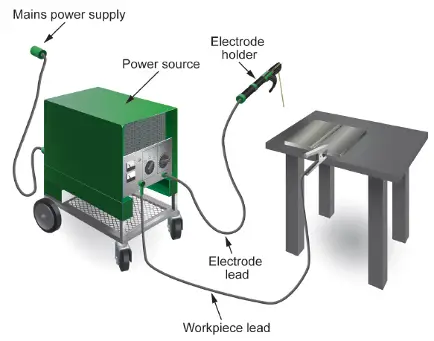
Electrical energy: Electrical energy is the most common source of energy for welding. It is used to make an electric arc or electrical resistance. This is usually done with the help of a welding power supply, which can be different sizes and have different amounts of power depending on the job.
Gas energy: In gas welding, the metal is melted and joined together by using the heat from a flame. The gas could be acetylene, propane, or some other gas that can catch on fire.
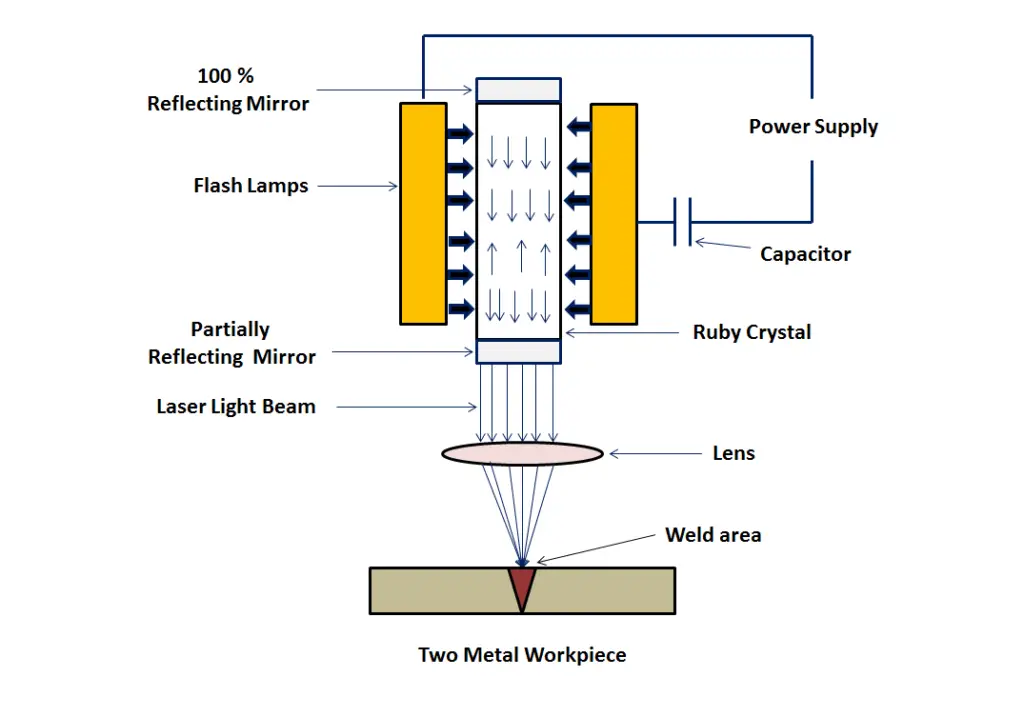
Laser energy: Laser welding uses a high-intensity laser beam to heat and melt the metal, which is then joined together. This is often used in places where accuracy is important, like in the aerospace industry.
Ultrasonic energy: High-frequency vibrations are used in ultrasonic welding to make heat and join metals together. This method is often used with plastics and other materials that aren’t made of metal.
Friction energy: In friction welding, the heat made when two metal pieces rub against each other is used to join them together. This is often used in industrial settings, like in the car business.
Overall, the type of energy source used for welding will depend on the job and how it will be done.
Final Talk
In the end, welding is a very important way to join two or more metal parts together by melting them and then letting them cool and stick together. Welding is used in many fields, like construction, manufacturing, and repair, to make metal structures that last and work well. There are different ways to do welding, such as arc welding, gas welding, and resistance welding. Each of these methods has its own benefits and uses.
Welding requires special tools, safety precautions, and skilled workers to make sure the products are safe and of good quality. As technology has improved, welding has become more efficient, less expensive, and better for the environment. Overall, welding is an important and useful skill that makes it possible to build structures that are important to modern life.
